 There are numerous theories and authors that incorporate the motivational concept of learning. The theories that are discussed here are not an all inclusive list that incorporate motivation in the theory.
There are numerous theories and authors that incorporate the motivational concept of learning. The theories that are discussed here are not an all inclusive list that incorporate motivation in the theory. Maslow's Hierarcy of Needs Theory: The Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory proposed that people have five different sets of needs: physiological needs, safety needs, love and belonging needs, esteem needs, and needs for self-actualization (Ormrod, 2008). Abraham Maslow's theory has a central feature of humanism and the basic needs of Maslow's Theory is the basis for motivation.
Achievement-Motivation Theory: Achievement-Motivation Theory was developed by Atkinson, McClelland, and Veroff and focuses on aspects of personality characteristics and proposes three forms of motivation or needs in work situations (McEwen, 2007). The three forms of motivation of the Achievement-Motivation Theory are achievement, power, and affiliation. The Achievement-Motivation Theory's central idea deals with the managerial success and motivation of a person.
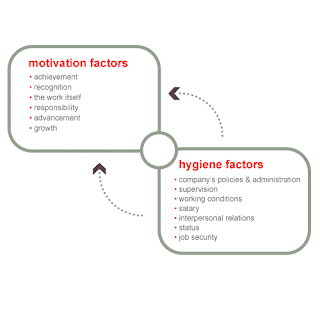
Herzberg's Theory of Motivation and Hygiene Factor: According to Frederick Herzberg's two-factor theory, some factors can lead to learning and satisfaction, while others do not in spite of resulting in dissatisfaction if they are absent altogether (What is Motivation, n.d.). Herzberg was primarily concerned with the people's well-being at work. Underpinning his theories and academic teachings, he was basically attempting to bring more humanity and caring into the workplace (BusinessBalls.com, 2010).
According to BusinessBalls.com (2010), examples of Herzberg's 'hygiene' needs (or maintenance factors) in the workplace are:
- policy
- relationship with supervisor
- work conditions
- salary
- company car
- status
- security
- relationship with subordinates
- personal life
Herzberg's research identified that true motivators were other completely different factors, notably:
- achievement
- recognition
- work itself
- responsibility
- advancement (BusinessBalls.com, 2010).
Herzberg's underlying concept was to increase motivation at work.
ARCS Model of Motivational Design by John Keller: John Keller is the author of this theory. According to Keller (2010) the ARCS model is a problem solving approach to designing the motivational aspects of learning environments to stimulate and sustain students’ motivation to learn. In order for this theory to be effective, motivation has to be used with instructional goals.
References
BusinessBalls.com. (2010). Frederick Herzberg motivational theory. Retrieved from http://www.businessballs.com/herzberg.htm
Keller, J. (2010). What is the ARCS model? Retrieved from
http://www.arcsmodel.com/Mot%20dsgn%20A%20model.htm
McEwen, M. and Wills, E. (2007). Theorectical basis for nursing. (2nd. ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins
Ormrod, J.E. (2008). Human learning. (5th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Merrill Prentice Hall.
What is Motivation? (n.d.). Theories of motivation. Retrieved from http://www.elmotivator.com/theories-of-motivation.html

No comments:
Post a Comment