THIS BLOG, ON MOTIVATION, WAS CREATED AS A PROJECT FOR NU600, A GRADUATE LEVEL NURSING PSYCHOLOGY COURSE AT THE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH ALABAMA -- SPRING, 2011.
Please leave comments by clicking on the "'comments" button under each section.
Motivational Quotes

Motivation Defined

Ormrod, J.E. (2008). Human Learning. (5th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Merrill Prentice Hall
Importance of Motivation


The importance of motivation is to keep it alive and not let it dwindle (About Balance and Control, 2007). Motivation needs reinforcement on a regular and ongoing basis to keep positive thinking alive. Sometimes it takes listening to a great motivational speaker, placing reminders, like a poster or sign, above your desk, or the use of medication or guided imagery. These tasks are done as daily maintenance for motivation and positive thinking. The importance of motivation and the use of motivational techniques are the secret to keeping the momentum moving forward once you start thinking positive (About Balance and Control, 2007). The key is to replace negative thoughts with positive thoughts to keep motivation alive. Replace thoughts of "I cannot do this!" with thoughts of "I can do anything I set my mind too!"
Usage and Application of Motivation
 According to Baker (2011), motivation techniques are essential for success in anything and any goal or aspiration requires a lot of effort and ability to overcome adversity. Motivation is the driving force that keeps you going towards your goal no matter how hard it is or how long it takes to success (Baker, 2011). Motivation takes positive thinking and action every day to meet a goal. Baker (2011) states that their are several techniques that one can apply to their life and career to succeed and keep you motivated:
According to Baker (2011), motivation techniques are essential for success in anything and any goal or aspiration requires a lot of effort and ability to overcome adversity. Motivation is the driving force that keeps you going towards your goal no matter how hard it is or how long it takes to success (Baker, 2011). Motivation takes positive thinking and action every day to meet a goal. Baker (2011) states that their are several techniques that one can apply to their life and career to succeed and keep you motivated: - Your goal as to be very specific, realistic and is able to be your main focus.
- Write a very specific vision or plan for the steps you need to take to attain this goal.
- Try difference motivation techniques that will work for you.
- Break down your plan into small segments that are more realistically reached.
- Make a "To Do" list every day. The first five are the most important tasks to be done that day.
- Reward yourself periodically. This reward will keep you positive.
- Do not lose focus just because you are not achieving your goals fast enough. Quitting is not an option.
- Have a trusted person keep you accountable and on track.
Baker, B. (2011). How to use motivation techniques effectively. Retrieved from http://ezinearticles.com/?How-to-Use-Motivation-Techniques-Effectively&id=1349887
Advantages and Disadvantages of Motivation
 Motivation by threat is a dead-end strategy and thus basically makes the staff or students more attracted to the opportunity side of the motivation curve than the threat side (What is Motivation, n.d.). Motivation, as discussed before, is divided into two types, extrinsic and intrinsic factors. For review, extrinsic motivation is any motivation that lies outside of the individual or task (such as receiving a paycheck for working). Intrinsic motivation is any source of motivation that lies within the individual or task (such as the person finds enjoyment or pleasure from a task).
Motivation by threat is a dead-end strategy and thus basically makes the staff or students more attracted to the opportunity side of the motivation curve than the threat side (What is Motivation, n.d.). Motivation, as discussed before, is divided into two types, extrinsic and intrinsic factors. For review, extrinsic motivation is any motivation that lies outside of the individual or task (such as receiving a paycheck for working). Intrinsic motivation is any source of motivation that lies within the individual or task (such as the person finds enjoyment or pleasure from a task). Advantages of extrinsic motivation: Extrinsic motivation more readily produces behavior changes and typically involve relatively little effort or preparation (Vanderbilt University: Center for Learning, 2011).
Disadvantages of extrinsic motivation: Extrinsic motivation can often distract students from learning the subject at hand and may be challenging to devise rewards and punishments. Over time, the rewards and punishments have to be escalated to achieve the same outcome (Vanderbilt University: Center for Learning, 2011).Advantages of intrinsic motivation: Intrinsic motivation can be long-lasting and self sustaining which typically promote learning and focuses on the subject rather then rewards or punishments (Vanderbilt University: Center for Teaching, 2011).
Disadvantages of intrinsic motivation: Intrinsic motivation efforts can be slow to affect behavior and may require special attention or preparation (Vanderbilt University: Center for Teaching, 2011).What is Motivation? (n.d.). What are the benefits of motivation? Retrieved from http://www.elmotivator.com/what-are-the-benefits-of-motivation.html
Vanderbilt University: Center for Teaching. (2011). Motivating students. Retrieved from http://cft.vanderbilt.edu/teaching-guides/interactions/motivating-students/
Theories and Authors of Motivation
 There are numerous theories and authors that incorporate the motivational concept of learning. The theories that are discussed here are not an all inclusive list that incorporate motivation in the theory.
There are numerous theories and authors that incorporate the motivational concept of learning. The theories that are discussed here are not an all inclusive list that incorporate motivation in the theory. Maslow's Hierarcy of Needs Theory: The Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory proposed that people have five different sets of needs: physiological needs, safety needs, love and belonging needs, esteem needs, and needs for self-actualization (Ormrod, 2008). Abraham Maslow's theory has a central feature of humanism and the basic needs of Maslow's Theory is the basis for motivation.
Achievement-Motivation Theory: Achievement-Motivation Theory was developed by Atkinson, McClelland, and Veroff and focuses on aspects of personality characteristics and proposes three forms of motivation or needs in work situations (McEwen, 2007). The three forms of motivation of the Achievement-Motivation Theory are achievement, power, and affiliation. The Achievement-Motivation Theory's central idea deals with the managerial success and motivation of a person.
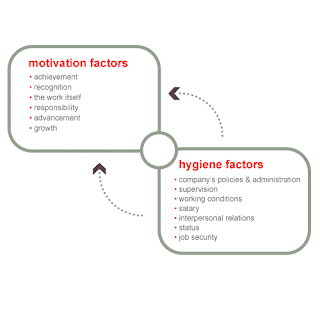
Herzberg's Theory of Motivation and Hygiene Factor: According to Frederick Herzberg's two-factor theory, some factors can lead to learning and satisfaction, while others do not in spite of resulting in dissatisfaction if they are absent altogether (What is Motivation, n.d.). Herzberg was primarily concerned with the people's well-being at work. Underpinning his theories and academic teachings, he was basically attempting to bring more humanity and caring into the workplace (BusinessBalls.com, 2010).
According to BusinessBalls.com (2010), examples of Herzberg's 'hygiene' needs (or maintenance factors) in the workplace are:
- policy
- relationship with supervisor
- work conditions
- salary
- company car
- status
- security
- relationship with subordinates
- personal life
Herzberg's research identified that true motivators were other completely different factors, notably:
- achievement
- recognition
- work itself
- responsibility
- advancement (BusinessBalls.com, 2010).
Herzberg's underlying concept was to increase motivation at work.
ARCS Model of Motivational Design by John Keller: John Keller is the author of this theory. According to Keller (2010) the ARCS model is a problem solving approach to designing the motivational aspects of learning environments to stimulate and sustain students’ motivation to learn. In order for this theory to be effective, motivation has to be used with instructional goals.
BusinessBalls.com. (2010). Frederick Herzberg motivational theory. Retrieved from http://www.businessballs.com/herzberg.htm
Keller, J. (2010). What is the ARCS model? Retrieved from
http://www.arcsmodel.com/Mot%20dsgn%20A%20model.htm
McEwen, M. and Wills, E. (2007). Theorectical basis for nursing. (2nd. ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins
Ormrod, J.E. (2008). Human learning. (5th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Merrill Prentice Hall.
What is Motivation? (n.d.). Theories of motivation. Retrieved from http://www.elmotivator.com/theories-of-motivation.html